Book Binding: The Journey from Manuscript to Bookshelf
The Evolution of Book Binding Techniques
From Scrolls to Casebound Volumes
Looking at how books have changed from ancient scrolls to today's hardcover editions tells quite a story about innovations in bookbinding. Back in the day, people used scrolls made from things like papyrus or animal skin. Rolling these up for storage made handling them pretty awkward. Everything changed when folks started using codices those little packages with pages stacked together and a spine holding them all. This wasn't just convenient it completely transformed reading habits because suddenly flipping through pages became possible, something we take for granted now. Then came Johannes Gutenberg with his movable type press around the 1400s. This game changer let books get produced much faster than before, and naturally, this affected how books were bound too. The whole industry had to adapt quickly to meet demand.
Casebound books represented a significant advancement in how we think about book design. What makes these books stand out is their ability to withstand wear and tear, thanks to those sturdy covers that protect the pages inside. People started noticing the visual appeal too, which helped boost their popularity across library systems and within publishing circles. The strength of the spine combined with covers that last for years means these books have become essential items for private collectors as well as institutions responsible for preserving valuable literary works.
Industrial Revolution's Impact on Binding
The Industrial Revolution really shook things up for book binding. All sorts of new machines started showing up in workshops back then, making the whole process way faster while driving down costs. Suddenly, publishers weren't limited by how many hands they had working on bindings anymore. What used to take days of careful handwork could now be done in hours. Machines such as the famous Jones & Smith model took automation to another level altogether. While these innovations definitely sped things up, interestingly enough they also allowed for some pretty impressive craftsmanship improvements too. Bookmakers found themselves able to produce higher quality work at volumes previously thought impossible.
Prior to all these tech breakthroughs, making books took forever and yielded very few copies. The whole process was painstaking work by hand, often taking months just to complete one volume. Things changed dramatically after the Industrial Revolution hit though. Suddenly shelves started filling up with books everywhere. Historical records show production numbers shot through the roof during this period. Factories began cranking out books at speeds no scribe could ever match. What's interesting is how this shift did two main things. First, it put knowledge within reach of regular folks who previously couldn't afford or access books. Second, it created entirely new systems and workflows that still form the backbone of today's publishing industry.
Hardcover Binding: Crafting Timeless Treasures
Smyth Sewing vs. Side Stitching Methods
When talking about hardcover books, there are basically two main ways they get put together: Smyth sewing and what's called side stitching. With Smyth sewing, the pages are sewn together right at their centers, so one section connects to the next in the middle. The result? A book that bends nicely and opens up completely flat on a table. Book publishers love this method because it lasts longer and makes reading much easier, especially important for coffee table books or art portfolios where people want to see every detail. Side stitching works differently though. Instead of connecting sections individually, the whole stack gets bound all at once through all those folded pages. This creates something really sturdy, perfect for books that get picked up and down constantly like school textbooks or reference materials found in libraries across town.
The choice between different binding methods really comes down to what the book will be used for and what the publisher wants. Take Smyth sewing for example this technique works great for those fancy publications where looks matter and pages need to lie flat when opened. We see it commonly in luxury photography books or beautifully designed fiction titles. On the flip side, most libraries and universities stick with side stitching because these books get handled so much they need something durable enough to survive years of constant use. The library world basically wrote the rulebook on this one after all their collections have been through decades of wear and tear.
Endpapers and Spine Reinforcement
Endpapers are pretty important in those hardcover books we all know and love, doing stuff that matters both practically and visually. These little pieces usually stick out from the very beginning and ending of the actual book part, giving extra strength to the back and keeping the whole thing from collapsing after years on someone's shelf. Some really nice endpapers actually make the whole book look better too, kind of like a sneak peek at what's inside. Think about those fancy coffee table books with colorful endpapers that just scream "look at me!" They set the tone for everything that follows between those covers.
What goes into reinforcing a book spine really matters when it comes to how long that book lasts on someone's shelf. Most publishers go with either cloth covers or those synthetic fiber options these days. Both have their pros and cons but generally strike a good middle ground between being flexible enough to open easily while still holding up against damage. For books destined to get lots of handling or end up in damp storage areas somewhere, having that sturdy spine makes all the difference. We've seen plenty of library copies fall apart after just a few months because they skipped proper reinforcement. The publishing world knows this too well, which is why many companies specify materials that won't crack under pressure and hold up through thousands of page turns over decades of use.
Flex Binding Innovations
Flex binding has become quite popular lately because it sits somewhere between regular hardcovers and those flimsy paperbacks we all know. The trick here is using lighter materials for the cover itself, so the book can actually bend without breaking but still holds up pretty well over time. People really love this stuff when they need something easy to carry around. Think about textbooks students tote back and forth or guidebooks travelers pack into already overcrowded bags. These aren't just any books either they're practical solutions for folks who want durability without the bulk.
Flex binding has become pretty popular because it works so well across different applications. Schools love how these bindings hold up against all the wear and tear from students flipping pages constantly throughout the day. Travel book companies are also big fans since they need something tough enough to survive backpacks but light enough not to weigh travelers down. We've seen a real shift in what people want from their books lately. More folks are asking for products that last longer without breaking the bank. Flex binding meets this growing need perfectly. Publishers who want to stay competitive are starting to see this format as both practical and innovative, bridging old school printing methods with modern demands for durability and convenience.
Perfect Binding for Modern Paperbacks
EVA vs. PUR Glue Technologies
When talking about perfect binding in paperback production, EVA and PUR glues stand out as key players in the market. EVA, or ethylene vinyl acetate, costs less money upfront so many small publishers go with this option when budgets are tight. But here's the catch - PUR adhesive, also known as polyurethane reactive, lasts much longer because of how it chemically bonds with materials. This makes PUR incredibly versatile too. It works well with all sorts of papers from thin newsprint to thick cardstock and holds up better against humidity changes and temperature swings. Most people stick with EVA for everyday books, but print shops working on premium titles like coffee table books or limited edition art collections will almost always choose PUR since these projects need bindings that won't fall apart after a few years on store shelves.
Layflat Paperback Advantages
Layflat paperback binding brings some real benefits, especially when it comes to how people actually use books. The main thing is that these books stay open flat on the table, something that makes all the difference for things like photo albums or technical manuals where flipping pages constantly gets old fast. With layflat binding, there's no weird warping or bending of pages when looking at pictures or diagrams, so everything stays nice and clear. That's why so many publishers gravitate toward this style for content packed with visuals. Take Amazon and Bluesky for instance they've been putting this binding method to good use in their instruction manuals. Readers get both functionality and decent looks from these publications, which isn't always easy to pull off in print media.
Specialized Book Binding Solutions
Custom Educational Flashcards for Interactive Learning
Custom made flashcards really boost interactive learning in classrooms and other educational environments. When teachers customize them according to what they're teaching and what students need to learn, these cards become much more than just study tools. They turn into fun, hands-on resources that actually grab kids' attention and get them involved in their own learning process. Creating good quality flashcards matters a lot too. Teachers should pick sturdy paper stock that won't tear easily and go for bright colors when printing so the cards stand out visually. The better looking and longer lasting the cards are, the more likely students will want to use them again and again. Studies show that students remember things better when they interact with physical objects like flashcards, plus they tend to stay engaged longer during lessons, which makes the whole experience both more fun and more productive for everyone involved.
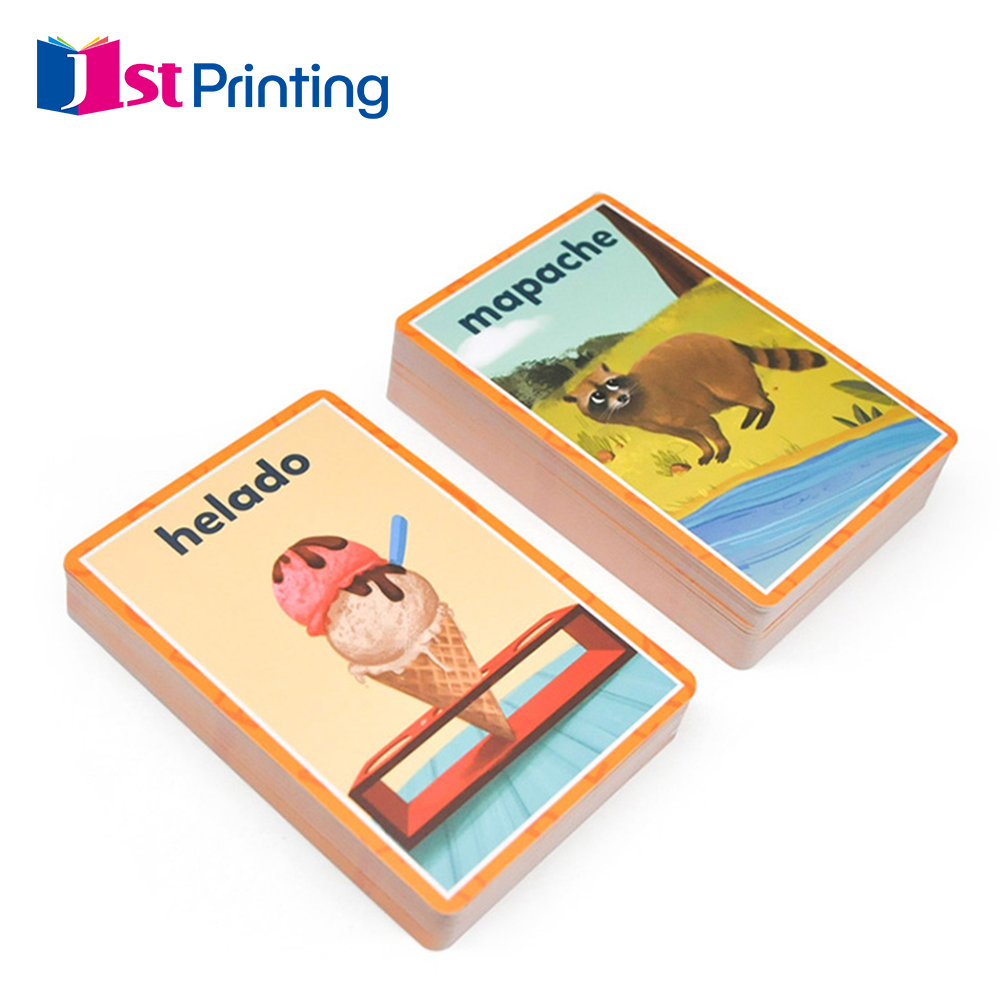

Personalized Hardcover Journals for Lasting Memories
People are buying more personalized hardcover journals lately because they let folks express themselves and keep special memories. Some folks use them just to write down thoughts, others fill them with drawings or sketches, while many appreciate having something organized where they can document important stuff. These journals come in all sorts of sizes, with different covers and paper types that really show off what someone likes. The way they're bound makes them last forever without looking cheap, which is why so many people actually use theirs every day instead of letting them collect dust on a shelf. When makers pay attention to how the pages are attached, it creates a nicer look overall and means the book opens flat when writing, making the whole experience much better for anyone who wants to get their ideas down on paper.
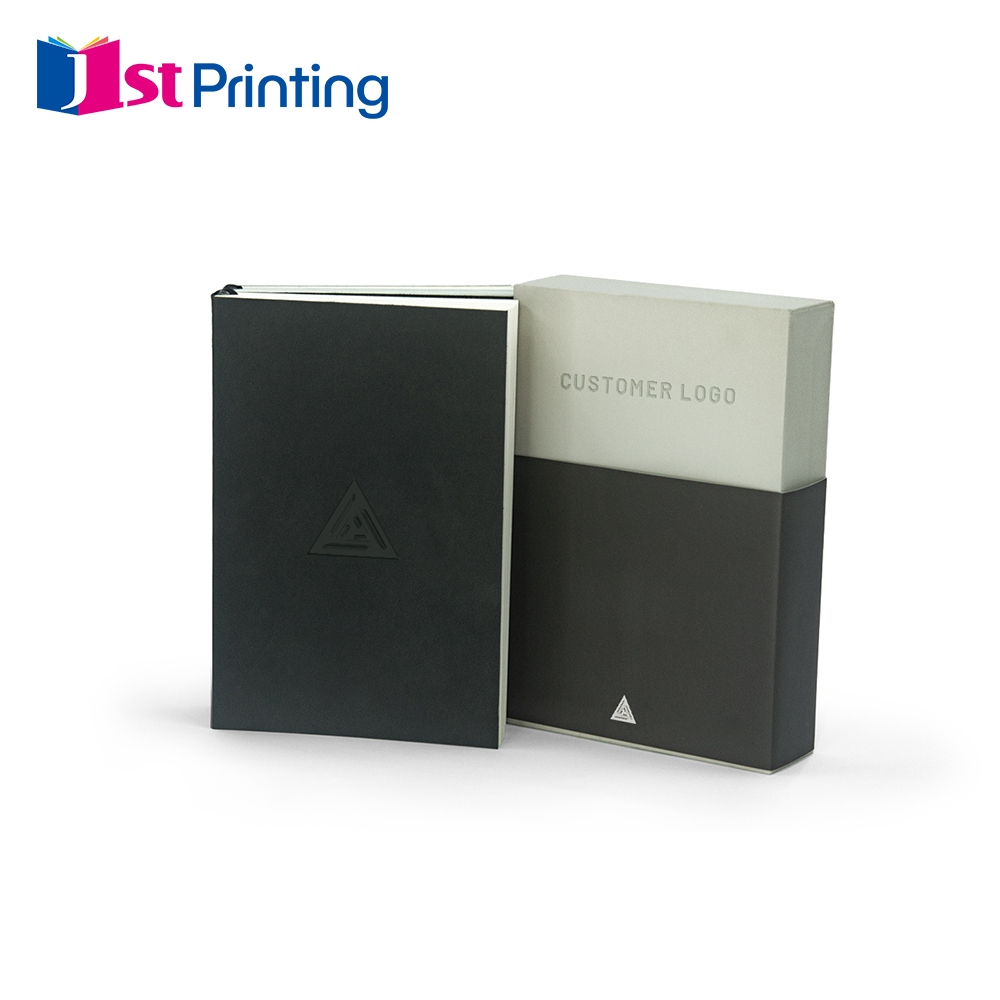

Spiral-Bound Planner Notebooks for Daily Organization
Spiral bound planner notebooks really shine when it comes to flexibility and how easy they are to work with, especially good for people trying to stay organized day to day. What makes these so great is how smooth page turning works, plus the fact that pages lie completely flat while taking notes. The spiral binding itself has become pretty much standard in quality planners because it holds up well over time yet still looks decent enough for most office settings. Anyone who flips through their planner multiple times throughout the day will appreciate not having to worry about tearing the binding as they rotate pages back and forth between meetings or appointments.

Digital Age Binding Innovations
Espresso Book Machine Capabilities
The Espresso Book Machine, or EBM for short, marks a real breakthrough in how we think about printing books. What makes these machines special is their ability to combine printing and binding into one process, so they can create quality books from digital files within just a few minutes. This tech has changed things quite a bit for book lovers everywhere, especially when it comes to getting hold of those hard-to-find titles or even making custom copies tailored exactly to what someone wants. For writers and smaller publishing houses, EBMs have been game changers because they cut out all the headaches that come with traditional mass printing methods. Industry folks report that these machines help save valuable floor space while cutting down on inventory expenses too. That means independent bookstores and public libraries can actually carry way more titles without needing massive warehouses full of paperbacks stacked to the ceiling.
On-Demand Printing Workflows
Printing books only when someone actually orders them has completely changed how publishers do business, making everything run smoother while cutting down on wasted paper and ink. Most companies now print titles just before shipping, which means no need to keep huge warehouses full of books nobody wants to buy. Industry reports show this approach is catching on fast across the board. What's interesting is how it matches what consumers want today too many people prefer getting exactly what they need right away rather than waiting weeks for something standard. Beyond saving money on storage space, this method creates a much cleaner production cycle since there's almost no chance of ending up with piles of unsold copies taking up room in basements everywhere. For publishers willing to switch gears, the savings on overhead costs plus renewed customer engagement makes all the difference, even if some traditionalists still grumble about losing control over print runs.